A high-quality world
created by light and vibration
Refresh Technology TL
Installation
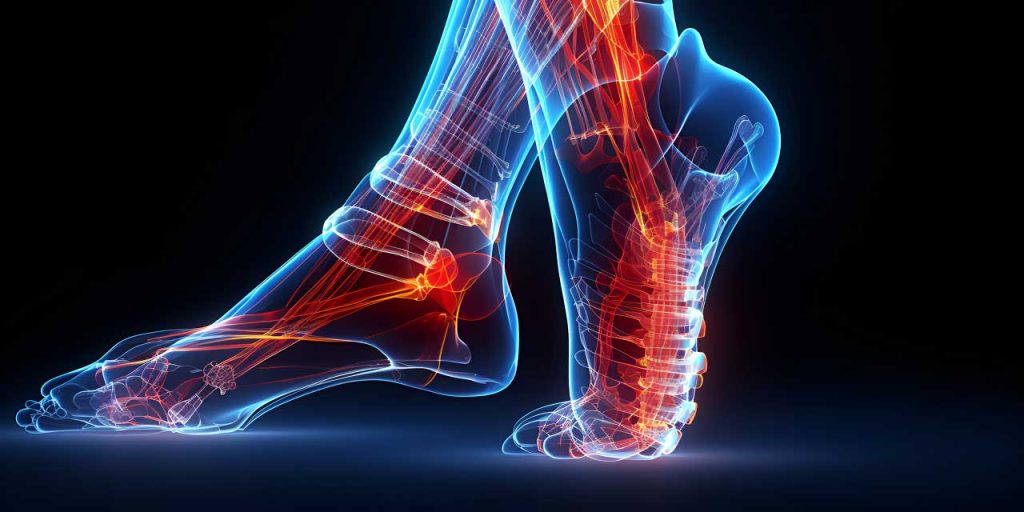
Introducing tolleru
Refresh Technology TL Installation
“tolleru“ is a machine that is effective for various physical disorders and beauty using light rays (Near Infrared and Visible Red) and special vibrations (fluid dynamics vibrations).(Patented)
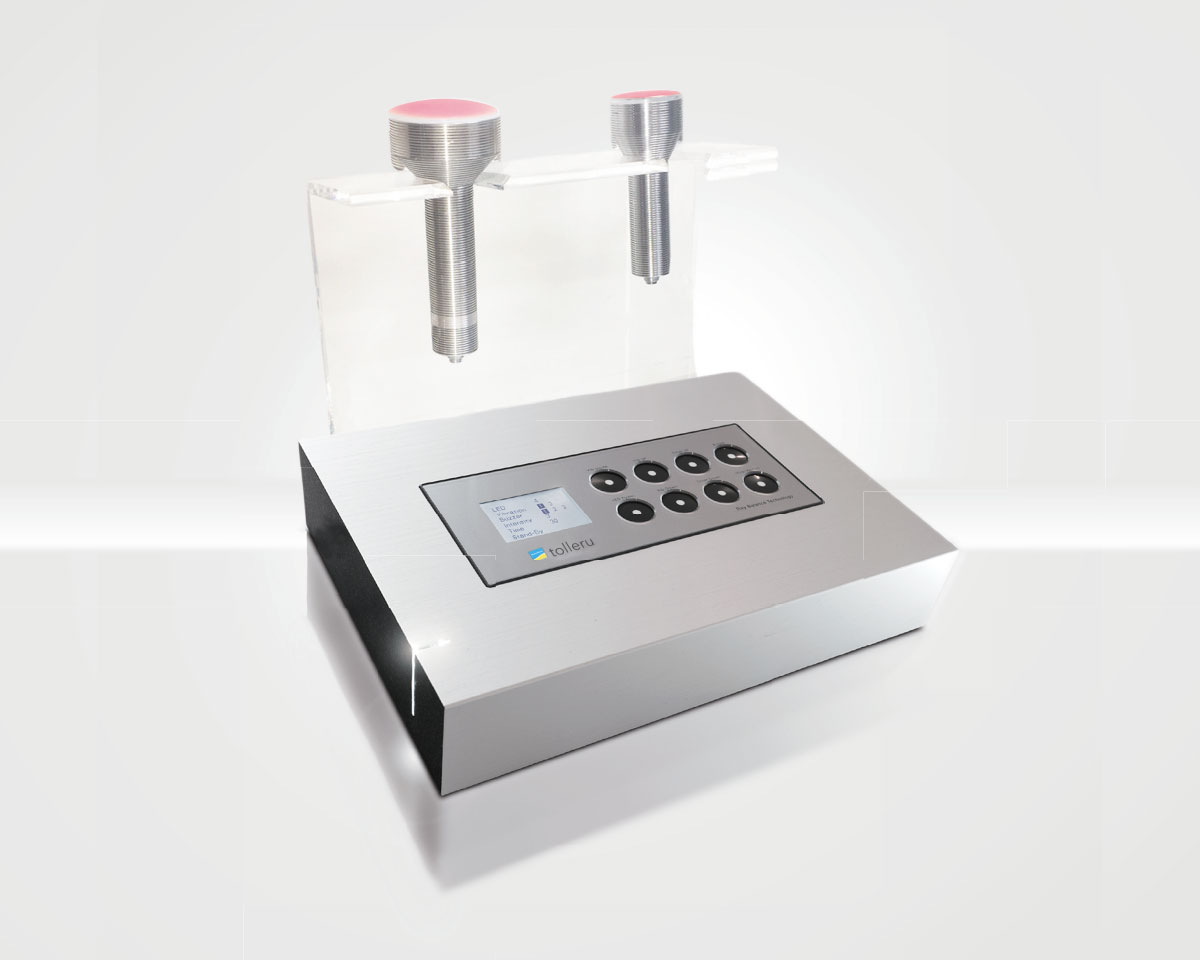

| Product | tolleru | |
|---|---|---|
| Spec | Size | 370mm x 260mm x 80mm |
| Weight | 3.2kg | |
| Power | IN 100-240V 50-60Hz 1.4A MAX OUT 24V 2.7A | |
| Power Consumption | 6-30W | |
| Peak Wave Length | NIR 855nm Red 630nm | |
| Motor | The voltage applied between terminals |
|
| Warranty Statemen | The warranty period is one year from the date of purchase. | |
| Repairment | Please contact the seller. During the warranty period, the seller will repair it according to the contents of the warranty certificate. For other details, please refer to the warranty card. | |
| After-Sales Service | ||
| If you have any questions about after-sales service, please contact the seller. | ||
| Development, design, production, and sales |
Nissho Hirano Co,.ltd Post Code 150-0013 3F Rembrandt Hiroo 2-13-10 Ebisu Shibuya-Ward, Tokyo TEL : +81-3-5422-9715 FAX : +81-3-6368-3682 https://refresh-technology.jp/eng/ https://nisshomh.jp/eng/ |
|
Effective Symptoms
- Low Back Pain (especially Golf)
- Stiff Shoulders
- Joint Pain
- Lumbago
- Release of Fascia and Muscle
- Trigger Finger
- Constipation
- Scalp Massage
- Promote Transdermal Drug Delivery (Hair Tonic and Cosmetics)
- Beauty (Especially Lift-Up, Skin Rejuvenation)
- etc.
Mechanism of the Effectiveness
- Effect of Near-Infrared and Red Visible Light
- Effect of Heat
- Effect as the Light
- Effect of Vibration
- Promotion of Capillary Blood Flow
- Effect of Transdermal Drug Delivery (TDD)
The Mechanism 1
- Heat Effect of NIR -
- HEMODYNAMIC EFFECTS ( Vasodilation )
When heat is applied to one area of the body, there is vasodilation where the heat is applied and to a lesser degree, systemically, in areas distant from the site of heat application. Superficial heating agents stimulate the activity of cutaneous thermoreceptors. It is proposed that transmission from these cutaneous thermoreceptors via their axons directly to nearby cutaneous blood vessels causes the release of bradykinin and nitrous oxide, and that bradykinin and nitrous oxide then stimulate relaxation of the smooth muscles of the vessel walls to cause vasodilation in the area where the heat is applied. This decrease in sympathetic activity causes a reduction in smooth muscle contraction, resulting in vasodilation at the site of heat application, as well as in the cutaneous vessels of the distal extremities. - NEUROMUSCULAR EFFECTS
- Changes in Nerve Conduction Velocity and Firing Rate
Increased temperature increases nerve conduction velocity and decreases the conduction latency of sensory and motor nerves. Nerve firing rate (frequency) has also been found to change in response to changes in temperature. The decrease in gamma neuron activity causes the stretch on the muscle spindles to decrease, reducing afferent firing from the spindles. The decreased spindle afferent activity results in decreased alpha motor neuron activity, and thus in relaxation of muscle contraction. - Increased Pain Threshold
Mechanisms of this effect include a direct and immediate reduction of pain by activation of the spinal gating mechanism and an indirect, later, and more prolonged reduction of pain by reduction of ischemia and muscle spasm or by facilitation of tissue healing.
- Changes in Nerve Conduction Velocity and Firing Rate
- METABOLIC EFFECTS ( Increased Metabolic Rate )
Heat increases the rate of endothermic chemical reactions, including the rate of enzymatic biological reactions. Increased enzymatic activity has been observed in tissues at 39°C to 43°C, with the reaction rate increasing by approximately 13% for every 1.0°C increase in temperature and doubling for every 10°C increase in temperature. Enzymatic and metabolic activity rates continue to increase up to a temperature of 45°C. - ALTERED TISSUE EXTENSIBILITY ( Increased Collagen Extensibility )
Increasing the temperature of soft tissue increases its extensibility. When soft tissue is heated before stretching, it maintains a greater increase in length after the stretching force is applied, less force is required to achieve the increase in length, and the risk of tissue tearing is reduced. Thermotherapy can be used clinically when the goals are to increase joint ROM and decrease joint stiffness. Mechanisms of this effect include the increased extensibility and viscoelasticity of periarticular structures, including the joint capsule and surrounding ligaments.
The Mechanism 2
- NIR Effect as the Light -
- PROMOTE ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE PRODUCTION
NIR and Red Light have been shown to improve mitochondrial function and increase their production of ATP by up to 70%. - PROMOTE COLLAGEN PRODUCTION
Light therapy is also thought to enhance tissue healing by promoting collagen production, likely by stimulating production of mRNA that codes for procollagen. Red light has been shown to promote an increase in collagen synthesis and mRNA production, and to induce a more than threefold increase in procollagen production. - PROMOTE VASODILATION
Some authors report that light can induce vasodilation, particularly of the microcirculation. This effect may be mediated by the release of preformed nitric oxide, which has been found to be enhanced by irradiation with red light. Such vasodilation could accelerate tissue healing by increasing the availability of oxygen and other nutrients, and by speeding the removal of waste products from the irradiated area. - ALTER NERVE CONDUCTION VELOCITY AND REGENERATION
Some studies have shown increased peripheral nerve conduction velocities, increased frequency of action potentials, decreased distal sensory latencies, accelerated nerve regeneration, and reduced nerve scarring in response to light stimulation, all of which indicate increased activation of nervous tissue by laser light. This effect has appeared to be more pronounced with red light than with blue or IR. These positive effects occur in response to light irradiation over the site of nerve compression and are enhanced by irradiation of corresponding spinal cord segments.
CLINICAL INDICATIONS FOR THE USE OF LASERS AND LIGHT
- TISSUE HEALING: SOFT TISSUE AND BONE
- ARTHRITIS
- LYMPHEDEMA
- NEUROLOGICAL CONDITIONS
- PAIN MANAGEMENT
The Mechanism 3
- Effect of Vibration -
Promotion of Capillary Blood Flow
In order to improve blood flow in the capillaries that are caused by poor circulation, NIR and Red light are useful. Which means the heat and the light are effective. And more improvement of the effectiveness needs fine vibrations. “tolleru” uses a different motor and trembler for each of the four probes. It enables the generation of special acoustic stream vibrations that match metal characteristics.
TDD
- Transdermal drug delivery -
- Generals
It is generally well known that vibrationing increases the speed of penetration and dissolution. In fact, Shaking(Vibration) is used when dyeing tissue in university laboratories. Because it is the safest and most reliable method. In addition, various methods (including devices) are used as a technology to promote TDD, but most of them damage cells. Therefore, “tolleru” uses vibrations for TDD. - TDD
The first thing you need to know about transdermal drug delivery (TDD) is: The skin (the stratum corneum) is a barrier, and hydrophilic and polymer liquids basically do not pass through. - Pathways of penetration of the skin barrier ( stratum cornea )
The first barrier of the skin is the outermost sebum of the stratum corneum. It passes through sebum and enters the stratum corneum and reaches the layer of granules below it. The route inside the stratum corneum is as follows.- Transcellular pathway (cell parenchymal permeation pathway)
- Intercellular route (intercellular space route)
- The follicular pathway (pores, etc.) < Highest absorption rate >
- Eccrine pathway (one of the sweat glands)
Reference
| Patent | Patented |
| Manufacture | Made in Japan |
| Technical site | https://refresh-technology.jp/eng/tl/ |
| Papers | https://refresh-technology.jp/eng/tl/effect-of-near-infrared/references/related-papers/ |
| How to Use | The Details of How to use are Fixed. |
